Heavy-Duty Screw Conveyor Selection Guide: Comprehensive Analysis of Equipment Parameters and Environmental Adaptability
2026-01-09
Application Tutorial
This article provides a systematic guide on selecting heavy-duty screw conveyors optimized for efficient, dust-free material handling. It thoroughly examines key equipment performance parameters, material characteristics, and the influence of conveying environments. The discussion emphasizes the advantages of heavy-duty screw conveyors in transporting powders, granules, and small lump materials, highlighting sealing technologies that minimize dust dispersion and contamination. The article also explores multi-point feed and discharge configurations that enhance production line flexibility. Combining industry challenges, technical insights, and practical case studies, it equips procurement and technical decision-makers with a sound basis for selecting conveyors that deliver high efficiency, safety, and low maintenance costs while improving operational and environmental standards.

Heavy-Duty Screw Conveyor Selection Practical Guide: From Equipment Parameters to Environmental Adaptability
Selecting a heavy-duty screw conveyor tailored for efficient, dust-free material handling is critical in industries managing powders, granules, and small lumps. This guide elaborates on the essential performance parameters, material characteristics, and environmental considerations that influence an optimal conveyor choice. Through careful analysis of screw rotor designs, sealed operation technologies, and multi-inlet/outlet configurations, businesses can improve operational efficiency while reducing maintenance costs and environmental impact.
Key Equipment Performance Parameters Explained
Understanding the core parameters of screw conveyors ensures alignment with operational goals:
- Conveying Distance: Typical heavy-duty conveyors range from 5 to 50 meters, with performance efficiency maintained up to 30 m without compromising throughput.
- Lifting Height: The vertical elevation capability often spans from 0 to 12 meters; selection depends heavily on plant layout and process flow requirements.
- Screw Rotor Design: Rotor geometry affects material flow and torque. Standard configurations (single or double flight) are optimized based on material abrasiveness and bulk density.
- Material Throughput: Load capacity scales with rotor diameter and pitch, typically between 0.5 to 10 m³/h for heavy-duty models.
Material Characteristics and Conveyor Suitability
Different materials require specialized conveyor adaptations due to their physical and chemical properties:
- Powders: Fine powders demand conveyors with enhanced sealing systems and smooth internal surfaces to prevent dust leakage.
Example: Cement or flour with particle sizes below 100 microns.
- Granules: Medium-sized particles such as plastic pellets are best conveyed with rotors designed to minimize particle degradation and provide uniform flow.
- Small Lump Materials: Irregularly shaped chunks (e.g., coal lumps, ore fragments) necessitate reinforced screw flights and robust shaft materials to withstand abrasion and impact.
Industry-standard ISO 5048 guidelines recommend rotor pitch ratios between 1:1 and 1:1.5 for abrasive materials to balance wear and throughput efficiency.
Environmental Adaptability and Structural Requirements
The operating conditions profoundly impact conveyor design choices:
- Dust Control Demands: Facilities emphasizing minimal environmental contamination mandate use of fully enclosed, sealed conveyors equipped with positive-pressure or vacuum extraction systems.
- Temperature Extremes: Materials transported at elevated temperatures require conveyors fabricated of heat-resistant alloys or equipped with cooling jackets.
- Corrosive Atmospheres: For chemical or salt-laden environments, corrosion-resistant coatings such as stainless steel grade 316 or special polymer linings are essential for enhanced longevity.
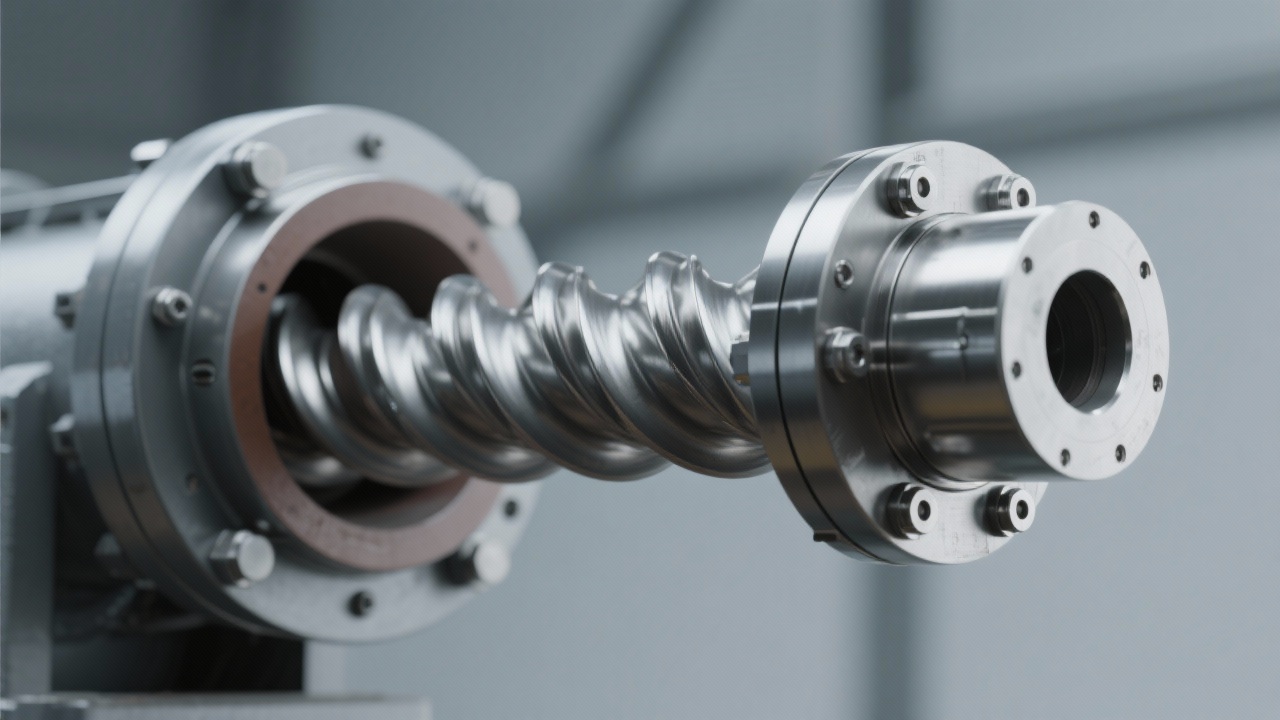
Sealed Operation Technology: Guarding Against Dust and Contamination
A primary challenge in powder and fine particulate handling is dust dispersion, which affects worker safety and product integrity. Advanced sealing solutions include:
- Labyrinth Seals: Employ multiple sealing rings to minimize dust escape while compensating for shaft movement.
- Air-lock Seals: Integrate pressurized air to create positive barriers preventing outward dust flow.
- Gland Packing and Mechanical Seals: Provide tight joints around rotating parts to maintain airtight operation.
Implementing these technologies results in visible reductions in workplace particulate concentration—by 40-60% in some case studies—significantly improving environmental compliance.
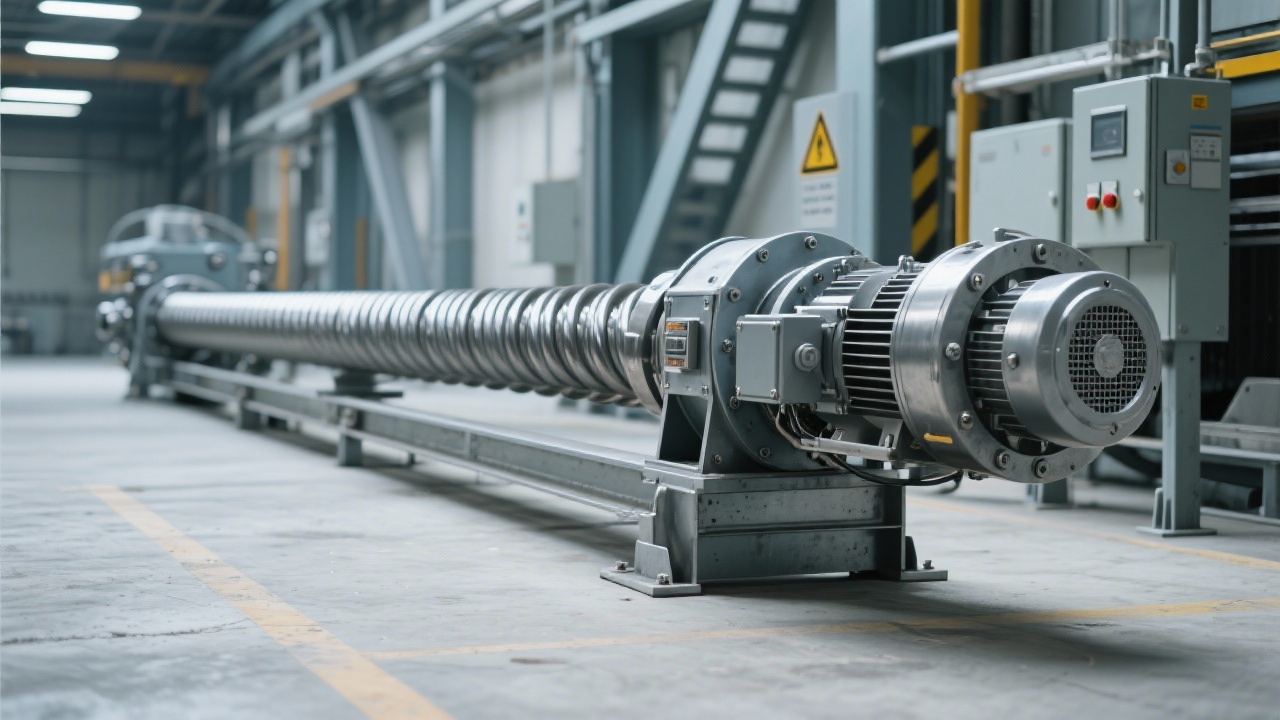

Multi-Point Inlet and Outlet Arrangements for Production Flexibility
Incorporating multiple inlets and outlets into screw conveyor systems provides several operational advantages:
- Enables simultaneous feeding from different production units, optimizing material flow.
- Allows discharge at multiple locations, reducing downstream bottlenecks.
- Enhances system adaptability for batch or continuous processing modes.
Customizable layouts improve production line responsiveness, thereby supporting lean manufacturing principles.

Practical Tips for Scientific Conveyor Selection and Maintenance
To maximize return on investment and operational reliability, industry practitioners should:
- Conduct thorough material testing to understand bulk density, moisture content, and abrasiveness.
- Specify rotor material and pitch based on abrasion resistance requirements.
- Validate conveyor capacity against daily throughput targets; allow a 10-15% safety margin.
- Plan routine inspection intervals focusing on sealing elements, shaft bearings, and motor performance.
- Implement predictive maintenance tools such as vibration monitoring to preempt equipment failure.
Note: A well-maintained heavy-duty screw conveyor can achieve operational lifespans exceeding 10 years in standard industrial settings.



